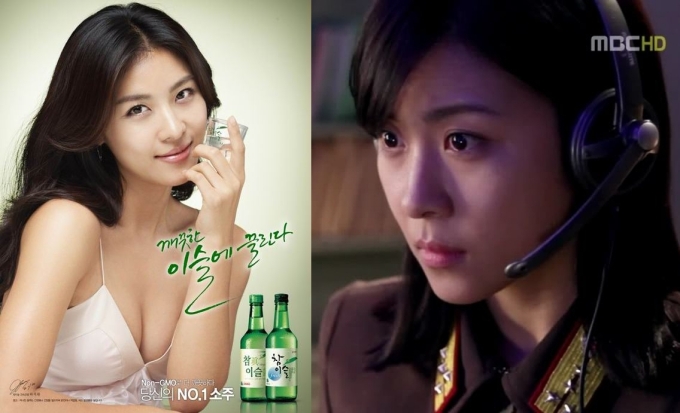
![SISTAR GOT CONSENT]() (Sources, edited: text, image)
(Sources, edited: text, image)
Give it to me, SISTAR.
Slip up just once while you’re promoting your new album, and give me your honest opinion of your costumes, your choreography, or your lyrics. Tell me what input you had in them. Tell me if you ever rejected those that Starship Entertainment provided for you.
Or did you waive that right when you signed your contracts?
Because several things are going to happen in the next few weeks: some people are going to slut-shame you for the lewdness of your performances, and some people are going to raise concerns about your sexual objectification. Some people might even do both.
![용감한 Producer 씨스타 Sistar]() And in all of those cases, the issue of your consent will be the elephant in the room.
And in all of those cases, the issue of your consent will be the elephant in the room.
First, because it’s both misogynistic and asinine to slut-shame you if you’re actually projecting a creation of your management company, rather than expressing your own sexuality and personality. Second, because as discussed back in April, there is both negative and positive (or benign) objectification, and the presence or absence of the consent of the person(s) involved is crucial for determining which is which (source, right):
According to Martha Nussbaum (1995; opens PDF) then: ‘In the matter of objectification context is everything. … in many if not all cases, the difference between an objectionable and a benign use of objectification will be made by the overall context of the human relationship (p. 271); ‘… objectification has features that may be either good or bad, depending upon the overall context’ (p. 251). Objectification is negative, when it takes place in a context where equality, respect and consent are absent.
On positive objectification, “dissident feminist” Camille Paglia is very much on point (my emphases in bold):
![SISTAR Bora]() Early on, I was in love with beauty. I don’t feel less because I’m in the presence of a beautiful person. I don’t go [imitates crying and dabbing tears], “Oh, I’ll never be that beautiful!” What a ridiculous attitude to take!–the Naomi Wolf attitude. When men look at sports, when they look at football, they don’t go [crying], “Oh, I’ll never be that fast, I’ll never be that strong!” When people look at Michelangelo’s David, do they commit suicide? No. See what I mean? When you see a strong person, a fast person, you go, “Wow! That is fabulous.” When you see a beautiful person: “How beautiful.” That’s what I’m bringing back to feminism. You go, “What a beautiful person, what a beautiful man, what a beautiful woman, what beautiful hair, what beautiful boobs!” Okay, now I’ll be charged with sexual harassment, probably. I won’t even be able to get out of the room!
Early on, I was in love with beauty. I don’t feel less because I’m in the presence of a beautiful person. I don’t go [imitates crying and dabbing tears], “Oh, I’ll never be that beautiful!” What a ridiculous attitude to take!–the Naomi Wolf attitude. When men look at sports, when they look at football, they don’t go [crying], “Oh, I’ll never be that fast, I’ll never be that strong!” When people look at Michelangelo’s David, do they commit suicide? No. See what I mean? When you see a strong person, a fast person, you go, “Wow! That is fabulous.” When you see a beautiful person: “How beautiful.” That’s what I’m bringing back to feminism. You go, “What a beautiful person, what a beautiful man, what a beautiful woman, what beautiful hair, what beautiful boobs!” Okay, now I’ll be charged with sexual harassment, probably. I won’t even be able to get out of the room!
We should not have to apologize for reveling in beauty. It is not a trick invented by nasty men in a room someplace on Madison Avenue….It is so provincial, feminism’s problem with beauty. We have got to get over this.
Granted, Paglia is unfairly homogenizing and stereotyping feminism, as my own favorite feminist scholar explains:
Few issues have caused more debate within feminism’s history than the sexualized representation of women….Feminist activists and scholars have long tangled with the issue of whether images liberate women from or enforce traditional patriarchal notions of female sexuality. From Laura Mulvey’s psychoanalytical constructions of the “masculine gaze” to Andrea Dworkin and Catherine MacKinnon’s longstanding appeals to broaden both cultural and legal definitions of pornography, there is a wide and influential range of contemporary feminist discourse on the ways in which women are manipulated and victimized through various cultural representations. These have led to a popular stereotype of the “feminist view” (if there ever were such a monolith) of the sexualized woman as a consistently negative one. However, the history and evolution of the women’s movement problematizes this stereotype, as women have actively demanded the right to act as free and discerning sexual subjects even as they may be interpreted or serve as another’s object of desire.
Yet be that as it may, in my experience there are precious few commentators on K-pop that heed Paglia’s imperative, let alone make any consent-based distinctions between negative and positive objectification. I’m especially frustrated with Korean commentators who, caveats about my article-searching skills aside, tend to view increasing sexual objectification — and/or sexualization — as a blanket evil, SISTAR usually only getting a mention as an example of this pernicious trend. Certainly, I’ve yet to find someone who bothered to find out if equality, respect and consent are indeed absent in your relationship with Starship Entertainment.
Then I remembered that if you want something done properly, you have to do it yourself.
So, I became your biggest fanboy, spending the last two weeks poring over all your interviews and TV appearances. Whereas I used to think that they were just mindless trash, and that you weren’t free to speak openly, I finally — belatedly — realized I could no longer simply assume either.
But ten-plus hours of videos, and numerous reading later? No offense SISTAR, but now I know they’re mindless trash.
I’ve learned, for instance, that: Bora has a mole on her left ear (32:37); Hyorin met her first love when she was in her second year of high school (7:10); all of them just love Las Vagas (7:00); there is an unofficial rule that band members can secretly start going out on dates once they approach 1000 days since their debut, but as of 973 days neither Hyorin nor Bora had (15:20); Hyorin has a pet snake; Soyou prepared for Christmas, 2011 by listening to a lot of carols (1:55); Dasom‘s mother is a big fan of the host of YHY’s Sketchbook (4:35); and so mindlessly on and on…
![Sistar Aegyo]() I would have watched more, but stopped paying much attention after watching one show that had you all spitting gum at a target for five minutes, and quit altogether after seeing the one above that opened with a pig shitting — which seemed a fitting metaphor for the quality of many of those programs. But most of all, I was giving up out of frustration at how many interviewers and TV show hosts would waste their precious time with you by almost always asking the same sort of inane questions, with the same predictable awww-we-love-you-[insert city/country/name of show]-guyz type answers (source, right).
I would have watched more, but stopped paying much attention after watching one show that had you all spitting gum at a target for five minutes, and quit altogether after seeing the one above that opened with a pig shitting — which seemed a fitting metaphor for the quality of many of those programs. But most of all, I was giving up out of frustration at how many interviewers and TV show hosts would waste their precious time with you by almost always asking the same sort of inane questions, with the same predictable awww-we-love-you-[insert city/country/name of show]-guyz type answers (source, right).
True: I am highlighting the most inane, the most vacuous, the most trivial parts of them. This may be patronizing and unfair: after all, some people are interested in such things, I’d probably be more interested myself if they were about Lee Hyori, and providing them is an integral part of creating and sustaining a fanbase. Also, the Sketchbook one is interesting in another way — albeit a negative one — for the disproportionate attention given to the handful of samchon (uncle) fans in the audience (5:50; that will have to be another post!). And I did learn via Soompi that perhaps you’re forced to wear short skirts:
SISTAR’s Soyu recently revealed her dislike of short stage outfits.
On the June 1 episode of “Beatle’s Code: Season 2,” Soyu honestly talked about the late controversies behind the group’s outfits.
![Park Han-byul short skirts high stools yoga school]() Soyu stated, “It is a little upsetting, it might be a good thing in a way. Even if we wear the same hot pants as other girl group members, when we wear them people call it racy. We think it’s because we have a healthy image so we try to think of it in a good way.”
Soyu stated, “It is a little upsetting, it might be a good thing in a way. Even if we wear the same hot pants as other girl group members, when we wear them people call it racy. We think it’s because we have a healthy image so we try to think of it in a good way.”
When asked if she liked wearing short skirts/dresses, Soyu answered, “I really hate wearing short skirts/dresses. Sometimes there are rude people who take photos from below us. There are even people who touch us with their hands.”
I’d add that sometimes PR people or press conference organizers will take advantage of this, only providing high stools for female celebrities to sit on (source, above-right). But Soyu, did you mean you would wear something different given the choice? Or that you just don’t like the perving? Why, oh why, didn’t the interviewer just ask?
And that was the best I got for 10 hours work. (Readers will surely understand why I’ll refrain from the addressing the post to SISTAR from this point!) But in hindsight, perhaps it was naive of me to expect anything more than frequently tantalizing — but always unsatisfying — hints, for several reasons.
![The Dazed and Confused Blogger October 29th 2011]() First, because I’ve already discussed the problem of Korean sources in my ongoing Who are the Korean Pin-up Grrrls? series. As always, I welcome readers’ suggestions for critical Korean commentary on K-pop; of course do know of, have read, and have translated some here; and acknowledge that my inability to find as much as I’d like doesn’t necessarily mean that there’s not more of it out there.
First, because I’ve already discussed the problem of Korean sources in my ongoing Who are the Korean Pin-up Grrrls? series. As always, I welcome readers’ suggestions for critical Korean commentary on K-pop; of course do know of, have read, and have translated some here; and acknowledge that my inability to find as much as I’d like doesn’t necessarily mean that there’s not more of it out there.
But frankly? As someone whose idea of a good time is to Google “성 상품화” after a couple of Black Russians, that caveat is sounding increasingly hollow and unnecessary.
Second, because for all the associations with the Korean idol and Japanese jumisho systems, as I’ll discuss in a moment, things are little different for Western performers:
Women have always felt the pressure to look decorative or pleasing, but within pop and rock, when the star is the focus of a mass gaze, this expectation is increased tenfold. In the face of the pop orthodoxy that a woman is there first and foremost to look attractive, female artists have consistently had to negotiate the Image issue. “There’s always what we call the Cleavage Question,” said singer Suzanne Vega. “How much to show, when to show it, if at all.”
While Cleavage was the main sexual barometer of the 80s, when pop was in its infancy, with 20s vaudeville blueswomen and 40s jazz swingers, focus was on the Leg. With 50s dream babes the emphasis may have been on the Derriere, as opposed to the fetishizing of the Hair in the 60s. Whatever the focus, the acceptability of women in pop has rested on their ability to read and wear the codes, to promote whatever body part is fashionable at the time.
Kate Bush provides an illustrative example:
An early shot from Kate Bush’s 1978 publicity campaign has her looking full-lipped and big-eyed, wearing a clinging vest, her nipples showing through. When asked about her image at the time, Bush insisted that she didn’t feel exploited. “I suppose the poster is reasonably sexy just ’cause you can see my tits,” she continued matter-of-factly. “But I think the vibe from the face is there….Often you get pictures of females showing their legs with a very plastic face. I think that poster projects a mood….I’m going to have trouble because people tend to put the sexuality first. I hope they don’t. I want to be recognized as an artist.”
Some years later, at the time of her third or fourth album, the penny dropped. “I was very naive and I was very young,” she said of the early photo sessions which led to her being one of the most popular ‘wank’ images to grace student bedrooms. “It was all very new to me and, in the first year, I learned so many lessons about how people wanted to manipulate me.”
(p.171; see 3rd paragraph down *here* also)
(Update: I really wanted to mention — but felt that the post already had more than enough quotes – “Selling an image: girl groups of the 1960s“ by Cynthia J. Cyrus in Popular Music, May 2003, as the similarities between Korean girl-groups of today and US and UK girl-groups of the 1960s are simply astounding. Please email me if you’d like a copy, or of any of the other journal articles mentioned here.)
![Taeyeon 25 No Boyfriend Needed]() Third, because it’s by no means only Korean reporters and TV hosts that are restricted in what they can ask Korean stars. As John Seabrook revealed in “Factory Girls: Cultural technology and the making of K-pop” in last October’s New Yorker, for instance:
Third, because it’s by no means only Korean reporters and TV hosts that are restricted in what they can ask Korean stars. As John Seabrook revealed in “Factory Girls: Cultural technology and the making of K-pop” in last October’s New Yorker, for instance:
Half an hour before the Anaheim show, I was backstage, on my way to meet Tiffany and Jessica, the two members of Girls’ Generation born and brought up in the U.S., who are both in their early twenties. An S.M. man was guiding me through the labyrinth of dressing rooms, where various idols, mainly guys, were having their hair fussed over and their outfits adjusted. There was a lot of nervous bowing. My minder hustled me along, telling me what questions not to ask the Girls. “Was it sad to say goodbye to your friends who didn’t make it?” he said. “Do you have a boyfriend?” He paused. “This is all going to Korea, and it’s a little different there,” he said. “So if we could stay away from the personal questions like boyfriends.”
(Update: Gag Halfrunt provides a second example in the comments)
Finally, because I watched Nine Muses of Star Empire (2012), an 82 minute documentary about Nine Muses’ life and training under management company Star Empire Entertainment, directed by Lee Hark-joon.
Or rather, I watched the 47 minute version that played on BBC World in mid-February (available here; it doesn’t embed well sorry), which by all accounts turned it into much more of a “journalistic exposé” than was originally intended, and certainly — deservedly — portrays Star Empire Entertainment in a very negative light. While SISTAR’s Starship Entertainment is of course a completely different company, I still probably wouldn’t even have bothered with their interviews if I’d first seen Nine Muses’ PR Manager (3:15) schooling them in exactly what to say at theirs, or their CEO (10:15) personally choosing — how empowering! — outfits that showed off their honey thighs:
![Nine Muses Honey Thighs]() That said, I do encourage readers to check out two interviews of the director, particularly in the latter link where he says:
That said, I do encourage readers to check out two interviews of the director, particularly in the latter link where he says:
Q) In the documentary the managers can be seen deciding on the girls’ outfits, songs and choreography. Do the girls have any say in their group’s concept, or is everything decided on for them?
A) The girls’ and boys’ band concept is decided by the agency. However, not all successful bands are like that. As they adjust to the music industry, they start composing their own songs and have more of a voice in their concept. In the documentary, the girls are told by managers: “If you become a star, your opinion is law. If you think you are treated unfairly, become a star.” What the manger said is cruel but it shows a reality.
Next, I insist readers check out at least Part One of — and especially the much longer comments to — W. David Marx’s series at néojapanisme on the Japanese jumisho system that the Korean idol system is based on, and which it’s clearly still very similar to. (The introductory chapter to Idols and Celebrity in Japanese Media Culture {2012} is also helpful, as is Googling “idol” and “Seoulbeats“; here’s a good starting post). Assuming that you have, then it’s an opportune moment to stop and take stock here:
![CL GQKR]() It’s difficult to find material on SISTAR specifically
It’s difficult to find material on SISTAR specifically- There is great variation in different management companies’ relationships with their employees/groups/artists. Star Empire Entertainment, T-ara’s Core Contents Media, and KARA’s DSP Media would be at one end of the scale, and probably 2NE1′s YG Entertainment and The Brown Eyed Girls’ Nega Network at the other.
- These relationships — i.e., level of groups’ freedom, autonomy, and involvement in their work — change over time, as indicated by director Lee Hark-joon above. To wit, SM Entertainment has reportedly improved in recent years, and just this week JYP announced that he no would no longer insist on having his name mentioned at the beginning of songs, and would allow his artists more freedom with composer choices
- Not being able to ask artists tough questions doesn’t preclude us from making informed guesses about their relationships with their management companies. Moreover, unfiltered news and confessions does appear all the time, After School’s UEE admitting just last week that their CEO effectively forced them to do (painful) pole dances in their latest MV for example, and CL on the right (source; edited) mentioning back in March that she refused her company’s requests for her to get cosmetic surgery before her debut (something YG would later do a complete 180 on). Likewise, I hope SISTAR will be more — er — revealing in the future too.
But where does all that leave the question of how to determine sexual objectification in K-pop?
Recall that in the last post, I provided some criteria on sexual objectification devised by various feminist scholars, and concluded that most purported examples in K-pop(and specifically, SISTAR’s Gone Not Around Any Longer MV and TV performances) didn’t meet those. Commenter ‘dash’ however, to whom I’m eternally grateful, pointed out that because of the levels of coercion involved in the idol system, then most likely idols did meet those criteria, even if — the main thrust of my post — sexy dancing and showing skin aren’t necessarily sexually objectifying — or rather, negatively sexually objectifying — in themselves.
To refresh readers’ memories, here are the seven specific criteria devised by Nussbaum, plus three more provided by Rae Langton:
- instrumentality: the treatment of a person as a tool for the objectifier’s purposes;
- denial of autonomy: the treatment of a person as lacking in autonomy and self-determination;
- inertness: the treatment of a person as lacking in agency, and perhaps also in activity;
- fungibility: the treatment of a person as interchangeable with other objects;
- violability: the treatment of a person as lacking in boundary-integrity;
- ownership: the treatment of a person as something that is owned by another (can be bought or sold);
- denial of subjectivity: the treatment of a person as something whose experiences and feelings (if any) need not be taken into account.
- reduction to body: the treatment of a person as identified with their body, or body parts;
- reduction to appearance: the treatment of a person primarily in terms of how they look, or how they appear to the senses;
- silencing: the treatment of a person as if they are silent, lacking the capacity to speak.
Applying academic theories to the real world is often messy and unsatisfying, but to conclude that we just don’t know if SISTAR are coerced by Starship Entertainment, so we just don’t know if #3, #7, and #10 apply, so we just don’t know if they’re negatively sexually objectified or not? It just felt galling, as if the last two weeks had been a complete waste.
It also presented quite an impasse, which took another two weeks to overcome.
For a while, it was tempting to leave it just at that, as you could argue that objective definitions are actually unnecessary, and/or seeking them misguided. After all, you’d think devising some for pornography would be much easier, but my (layperson’s) impression is that despite laws distinguishing between its many forms, and despite various coda used by law enforcement agencies to police, say, child porn (for example, the COPINE scale), we’re actually no closer to having objective definitions of it than when Supreme Court Justice Potter Stewart famously said in 1964 (albeit later retracted and regretted) that it was hard to define the hard-core stuff, but that he knew it when he saw it.
Perhaps, that’s because the world’s first peer-reviewed academic journal on pornography won’t even be launched until next year?
In contrast, Buszek’s quote above reminds us that academic work on objectification has a long pedigree, and is indeed the primary means — and likely will remain the primary means — by which we discuss “the ways in which women are manipulated and victimized through various cultural representations.” And who could doubt it the necessity of doing so, after watching the following video?
Not what it may seem, Escher Girls describes it as:
A video about the straight cis male gaze in cinema (and video games), examples of it, and talking about how even when men are sexualized on screen, it’s still as active agents and not as a collection of body parts where the camera zooms in and cuts to various secondary sex characteristics. Not a new concept, but the video is still interesting, even as just food for thought.
I also think having it deconstructed visually like he does, helps one pay a little more attention to how the world around us is constructed via the media we consume, in even small subtle ways, like where the camera focuses, pans, and zooms in on, and the difference between cuts that show pieces of the body versus full face & body shots.
….Also, this doesn’t mean it’s NEVER a thing to do, sometimes it can be used very effectively, and increases the understanding of a scene…but it’s when it becomes the norm of depicting women in all situations…
So, after two weeks of banging my head against a brick wall, it finally occurred to me to Google PDF files with “sexual objectification” in the title. In just five minutes of looking, I came across the solution in the form of “Sexual Objectification of Women: Advances to Theory and Research” in The Counseling Psychologist 39(1), 2011, pp. 6-38 by Dawn Szymanski, Lauren Moffitt, and Erika Carr, as I was immediately struck by how their five core — but very interrelated — criteria of a “sexually objectifying environment” were eerily similar to life in a management company:
A) Traditional gender roles exist
The first thing that came to mind upon reading this were the traditional gender roles perpetuated by a significant number — but by no means majority — of songs and MVs by girl-groups, buttressed by the ridiculous double-standards of Korean censors. But, while that’s certainly something worth exploring, it’s more appropriate to focus on the environment in which management company employees work in.
Especially as this is a concept originally devised for places like Hooters (pp. 21-22):
![Hooters Korea]() Specific to the workplace, [one researcher] used the term gender role spillover to refer to the carryover of these traditional gender roles into work environments where they are irrelevant or inappropriate. This phenomenon is more likely to occur when gender role is more salient than work role and/or gender ratios are highly skewed, because under many circumstances, individuals use gender role stereotypes to guide behavior, especially in male-female interactions. In particular, gender role spillover occurs when women (more than men in similar occupational roles) are expected to project their sexuality through behavior, appearance, or dress. When gender role spillover occurs, the effects may be magnified when women hold jobs where one aspect is reminiscent of a sex object (i.e., cocktail waitress). In this position, women are likely to be targets of unwanted sexual attention but may (inaccurately) attribute the way they are treated to their job rather than to their gender. A dynamic is then set up where men are expected to take the role of sexual initiator. One potential outcome is a sexualized work environment where sexual remarks, seductive clothing, and sexual advances are tolerated and encouraged.
Specific to the workplace, [one researcher] used the term gender role spillover to refer to the carryover of these traditional gender roles into work environments where they are irrelevant or inappropriate. This phenomenon is more likely to occur when gender role is more salient than work role and/or gender ratios are highly skewed, because under many circumstances, individuals use gender role stereotypes to guide behavior, especially in male-female interactions. In particular, gender role spillover occurs when women (more than men in similar occupational roles) are expected to project their sexuality through behavior, appearance, or dress. When gender role spillover occurs, the effects may be magnified when women hold jobs where one aspect is reminiscent of a sex object (i.e., cocktail waitress). In this position, women are likely to be targets of unwanted sexual attention but may (inaccurately) attribute the way they are treated to their job rather than to their gender. A dynamic is then set up where men are expected to take the role of sexual initiator. One potential outcome is a sexualized work environment where sexual remarks, seductive clothing, and sexual advances are tolerated and encouraged.
(Update: See here for more on Hooters in Korea {source, above})
B) A high probability of male contact exists (physically speaking, a male-dominated environment)
Here, the authors’ meaning is the greater numbers of men compared to women in the environment in question; lacking that data, this cannot be confirmed or denied in the case of Korean management companies. But we can guess — and this is confirmed by Nine Muses of Star Empire — that the female idols do have considerable contact with the same few men, and…
…the extent of contact with men [is] a key predictor of incidence of harassment, number of different types of harassment, sexual comments, sexual categorical remarks, and sexual materials for women. Thus, contact with men may serve as a mediator between women and sexual objectification (SO). Frequent contact with men may create a more sexualized environment, which in turn allows for more SO experiences. (pp. 22-23)
Next, consider the disproportionate power of those men:
C) Women typically hold less power than men in that environment
This can be taken as a given. But Seabrook puts it well, and the combination he describes is covered well in the comments to Part One of the jumisho series at neojaponismé:
When you replicate the American entertainment business, and add the Confucian virtue of rigid respect for elders to the traditionally unequal relationship between artists and suits, the consequences can be nasty.
I’d also add that although men can and do write, direct, and/or produce — for want of a better word — feminist songs and MVs, and that although those intended for heterosexual men can be willingly embraced by women (of all sexualities) nevertheless, the example of lyricist Kim Eana (and others) points to the common-sense conclusion that the more women in the industry, the more feminist and/or positively-objectifying songs and MVs will likely be produced.
The final two are also self-evidently true:
D) A high degree of attention is drawn to sexual/physical attributes of women’s bodies
Environments where women are required, often by specifications of a uniform, to reveal and emphasize their bodies are clearly sexually objectifying. Additionally, wearing tight or revealing clothing may facilitate self-objectification, as women constantly review their appearance and the fit of their clothing in the surrounding mirrors. Supporting this notion, [one study] found that women in fitness centers who wore tight and fitted exercise clothing (gym tops and gym pants) placed greater emphasis on their appearance attributes and engaged in more habitual body monitoring than women who wore looser clothing (T-shirts and sweatpants). Relatedly, [other researchers] found that the attention focused on women’s bodies in fitness centers leads women to self-objectify more. (p. 23)
E) The approval and acknowledgement of male gaze
![세상을 바꾸는 퀴즈 현아]() …girl watching is a “targeted tactic of power” where men use gaze to demonstrate their right to physically and sexually evaluate women. The activity serves as a form of playing a game among some men; however, the targeted woman is generally understood to be an object, rather than a player, in the game. Thus, from a male point of view, “acts such as girl watching are simply games played with objects: women’s bodies”. The effects of male gaze on women may be intensified by the accompaniment of sexually evaluative commentary. (p. 24; source, right)
…girl watching is a “targeted tactic of power” where men use gaze to demonstrate their right to physically and sexually evaluate women. The activity serves as a form of playing a game among some men; however, the targeted woman is generally understood to be an object, rather than a player, in the game. Thus, from a male point of view, “acts such as girl watching are simply games played with objects: women’s bodies”. The effects of male gaze on women may be intensified by the accompaniment of sexually evaluative commentary. (p. 24; source, right)
And with that, I could finally conclude my month-long inquiry. Which in short, is that I now more or less agree with dash(!), the commenter that started me on it. Or in full, that:
- Given everything we know about the idol system, it is fair to assume that management companies are sexually objectifying environments
- Consequently, it fair to assume that female performers do not always consent to the sexual objectification asked of them
- Consequently, it is negative sexual objectification
- And crucially, if the management companies and/or performers feel that these assumptions are incorrect and unfair, that the onus is on them to prove us feminist whiners wrong
As many do…
Yes, you can argue that that’s a lot of assumptions. And/or that, because the first set ivory tower criteria from the last post didn’t work in the real world, that I’ve merely gone and replaced them with another. Both criticisms are fair. Also, I acknowledge the very very broad range of topics above, and am aware of the many exceptions, over-generalizations, and just plain simple mistakes involved in covering them all. I welcome and appreciate readers pointing them out to me, and look forward to discussing them in the comments.
![SISTAR give it to me please]() Yet most of all, I’m happy that I now longer feel so stymied, feel so…inadequate when talking about objectification in K-pop because I feel I won’t ever been able to hear enough about it — or indeed, anything about it — from the singers themselves.
Yet most of all, I’m happy that I now longer feel so stymied, feel so…inadequate when talking about objectification in K-pop because I feel I won’t ever been able to hear enough about it — or indeed, anything about it — from the singers themselves.
Of course, the drudgery of religiously scanning news reports and interviews for their voices — i.e. to make assumptions into facts – is still essential, and, having recognized that, motivated fanboying is something I definitely plan to continue doing in the future. But spending hours toiling over, say, all 114 pages of the SISTAR tag on allkrap allkpop for those slip-ups before you can feel you can even write? Really, us feminist whiners can do much better than that.
And SISTAR, so can you too. Give it to me indeed.
You know what I mean!
![]()
p.s. Like this post? Did it keep you occupied for half an hour? Please consider making a small donation, to help me write more of them — I’ve only had one two so far this year! ㅠㅠ
Filed under:
Girl Groups,
Korean Game Shows,
Korean Magazines,
Korean Media,
Korean Music,
Korean Newspapers,
Korean Sexuality,
Korean Talk Shows Tagged:
스타쉽 엔터테인먼트,
씨스타,
씨스타19,
SISTAR,
SISTAR19,
Starship Entertainment ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![Korean Movie Censorship]() (Sources, edited: left, right)
(Sources, edited: left, right)